The symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis depend on which vertebrae have suffered dystrophic damage and their severity depends on the changes that have occurred in it. An experienced specialist, after hearing the patient's complaints, will be able to make the correct diagnosis and suggest which part of the spine has undergone serious change and destruction. The sooner a doctor diagnoses thoracic osteochondrosis and prescribes medication, the sooner relief will come.
Thoracic osteochondrosis is much less common than cervical osteochondrosis, as the thoracic spine is less prone to stress and deformity. However, it provides a lot of pain and discomfort and has a variety of symptoms.
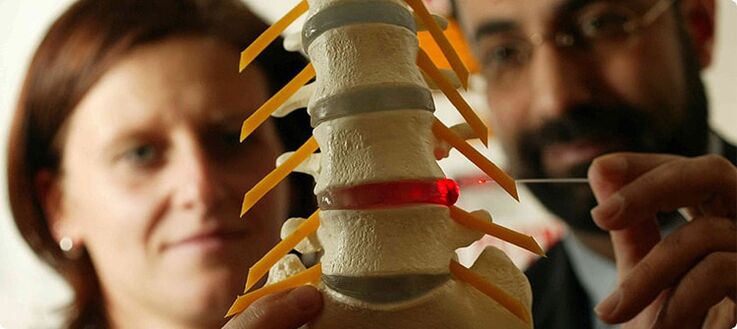
Chest osteochondrosis, symptoms and signs
The pain is located mainly between the shoulders or in the intercostal space. Often, thoracic osteochondrosis manifests as pain in the lumbar region of the body. Patients describe such pains with the feeling of a "stake in the chest", their mobility is disturbed, since the pain penetrates with the slightest careless movement. The pain is aggravated by coughing, sneezing, deep breathing and torso twisting. Shortness of breath occurs, breathing becomes shallow and frequent. It is very difficult for the patient to raise his arms or lean, as this causes sharp and intense pain. The vibration of the body also causes discomfort, ie driving a bicycle, car on an uneven road, as well as any jumps. Cooling of the body can cause an exacerbation of pain, and even with proper treatment, the disease can begin with renewed vigor.
Often the pain is located in the gaps between the ribs. This is due to compression of the nerve roots, which leads to intercostal neuralgia. The sensations of pain become more intense at night, when he turns from side to side or changes position, the patient wakes up from an acute penetrating pain, even despite the treatment with painkillers.
Sweating, fatigue and rapid fatigue are associated with signs of pain, sometimes there is a rise in temperature locally above the inflamed part of the spine.
Signs of dorsago and dorsalgia
The strong and very acute pain is called dorsago. With thoracic osteochondrosis, the symptoms of the back appear in people who sit still for a long time in a sloping position of the body forward. With a sharp rise or change of position, the body is pierced by an acute pain. It is so loud and unexpected that it takes your breath away and makes it difficult to breathe. The muscles of the chest and back become like a stone, sometimes puncturing with cramps. The treatment alleviates the pain and brings relief to the patient.
The dorsal, on the other hand, is a pain of a painful nature. It is not very intense, but it constantly reminds itself. With sudden and rapid movements, coughing, sneezing or deep inspiration, the body also pierces with acute lightning pain. The twists and turns of the body are also given with difficulty and pain. The muscles of the back and chest are stretched and the feeling dominates, as if the upper part of the body is being pulled by a belt.
To temporarily relieve or relieve the pain from these pains, sometimes it is enough to walk or do a light workout.
Signs of a neurological nature in osteochondrosis
Most often, osteochondrosis of the thoracic region occurs, symptoms of a neurological nature. This is manifested by a "goose" sensation or loss of sensation in the abdomen or upper chest. Sometimes patients notice tension or stiffness of the muscles of the back, mainly the upper part, as well as the chest. In more severe and advanced cases, there is a violation of the work of the pelvic organs.
In men and women, thoracic osteochondrosis develops in much the same way and the symptoms are similar. The only difference is that women have a later onset of the disease. Women are prone to this condition during menopause. This is due to the reduction of the hormone progesterone, which protects the spine or rather the spinal discs from wear and tear.
With osteochondrosis, a woman may have strange symptoms, such as flaking of the skin and brittle nails. Women find it more difficult to tolerate both thoracic and cervical osteochondrosis due to the lower pain reduction of the weaker sex.
Men, on the other hand, go to specialists with osteochondrosis of the thoracic region many times more often than women and the average age is about 30-40 years. Men may complain of decreased strength. The most important thing here is to confess the problem to the doctor and not to deal with it alone.
Signs of osteochondrosis that can be confused with other diseases
Since there are many nerve fibers and extremities in the chest area, therefore, the pain behind the sternum can radiate in any direction. The symptoms of osteochondrosis are very similar to those of other diseases, which worsens the condition with the diagnosis. Early diagnosis of osteochondrosis and initiation of treatment is very important for the most favorable outcome of the disease.
Many people confuse osteochondrosis with heart disease. But here it is worth remembering some differences. First, with thoracic osteochondrosis, the pain is greater over time and cannot be treated with heart medication. And the second sign is that there is no increase in blood pressure, as is often the case with a disease of the cardiovascular system. Most importantly, the ECG results show no abnormalities in the work of the heart.
In women, the pain can spread to the mammary glands and this sign of thoracic osteochondrosis is very common. In this case, it is necessary to consult a mammologist and rule out a disease of the mammary glands.
Sometimes the patient complains of pain in the epigastric region, which can be confused with gastritis or stomach ulcer. Pain can also be found in the right hypochondrium and non-specialist medical staff may suspect cholecystitis or pancreatitis. With lower abdominal pain, appendicitis may be suspected. In such cases, additional ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs, radiography and EGD of the stomach and, of course, clinical blood test are recommended.
If the lower part of the thoracic spine is affected, the patient will have signs of intestinal diseases. But this condition does not depend on the food taken and the pain is aggravated by exercise.
If osteochondrosis has affected the upper part of the spine, then the pain will spread to the pharynx and esophagus. The patient will feel foreign body marks in the throat and there may be difficulty in swallowing food, especially insufficiently chewed.
Only a doctor should deal with the diagnosis and treatment, self-medication in this case is unacceptable.
The effect of the profession on the development of osteochondrosis
The peculiarities of certain professions can develop osteochondrosis. This is due to the sedentary lifestyle, especially in professions such as truckers, pilots, engineers. And also in the risk group are professions related to lifting weights, for example, loaders. With prolonged lifting and transport of large loads, rubbing and flattening of part of the vertebrae occurs, which also leads to osteochondrosis not only of the thoracic, but also of the cervical and lumbar part of the spine. In more advanced cases, the arms or back begin to numb closer to the shoulder area. This is a wake-up call to contact a specialist for examination and treatment.
Most office workers are prone to cervical osteochondrosis. That is, not only the vertebrae of the thoracic region are involved in the process of change and destruction, but also the cervical vertebrae. Prolonged sitting at computers, even in the wrong position, leads to weakening and flabby muscles that support the spine. The vertebrae begin to shift, biting the nerves.
Also, being immobile in one place, the blood flow of the intervertebral discs is disturbed, which leads to starvation of the disc tissues and their destruction. They feel pain in the head, shoulders and chest. They have hearing loss and tinnitus. With a sharp rise or movement of the head, the worker may lose consciousness as the work of the vestibular apparatus is disturbed. Vision is often impaired and flies appear in front of the eyes. The muscles of the shoulder girdle and chest begin to ache, as after a long workout.
It happens that after the treatment it is worth changing your profession, as there are frequent relapses in the old workplace.

































